The reasons for removing a page from Google search results have not changed much since I first published this article in 2023. Examples include sites with confidential, premium, or outdated information. Still, tools and tactics have evolved.
Here is my updated version.
Temporary removal
The need to remove URLs from Google is urgent when a site (i) is infected with malware or illegal content during indexing (even ranking), or (ii) inadvertently reveals private information that the search giant then indexes.
The fastest way to hide URLs from searchers is to use Google’s URL Removal Tool in the “Indexing” section of Search Console. Here you can delete a single URL or an entire category.
In my experience, Google processes these requests quickly, but does not permanently index them. Instead, it hides URLs from search results for about six months.
Search Console has been removing URLs from search results for “about six months.” Click image to enlarge.
A similar feature in Bing Webmaster Tools called “Block URLs” will hide pages from Bing searches for about 90 days.
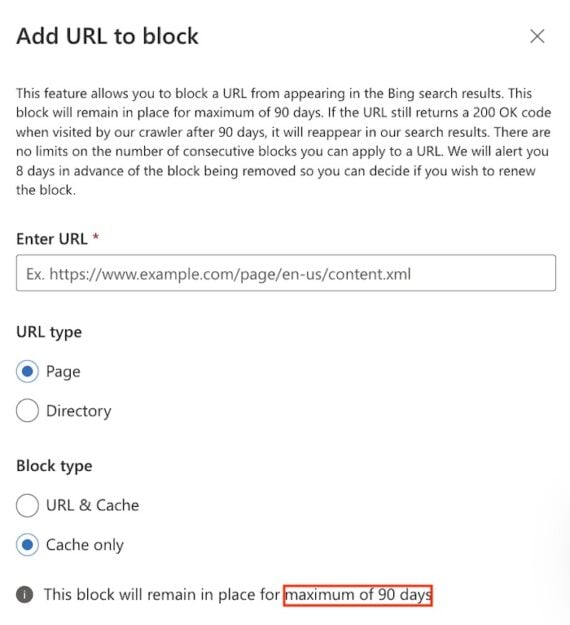
“Block URLs” in Bing Webmaster Tools will hide pages from Bing searches for approximately 90 days. Click image to enlarge.
Permanent
Several options permanently remove URLs from Google’s index.
Remove the page from your site
Deleting a page from your web server will permanently unindex it. After deletion, set HTTP status code 410 to “removed” instead of 404 “not found”. Wait a few days for Google to crawl the site again, detect the 410 code, and remove the page from the index.
Note that Google does not recommend using redirects to remove low-value pages, as this practice sends the wrong signals to successors.
In addition, Google provides a form to remove personal data from search results.
Add noindex label
Search engines are almost always honored noindex meta tag. Search engines will crawl a noindex page but will not include it in the search results.
In my experience, Google immediately recognizes a noindex meta tag once the page is traversed. Note that a tag removes a page from search results, not a website. The site remains accessible through other links, both internal and external.
The noindex tag probably won’t remove a page from LLMs like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity because these platforms don’t always respect noindex tags or even robots.txt exclusions. Deleting pages from your website is a safe removal tactic.
Password protection
Consider adding a password to the published page to prevent public access. Google cannot crawl sites that require passwords or usernames.
Adding a password will not remove the indexed page. HAS noindex tag will however.
Remove internal links
Remove all internal links to pages you don’t want indexed. And don’t link to password-protected or deleted pages; both hurt the user experience. Always focus on human visitors – not search engines themselves.
Robots.txt
Robots.txt files can prevent Google (and other robots) from crawling a page (or category). Pages blocked by robots.txt can still be indexed and ranked if included in a sitemap or otherwise linked. Google doesn’t come across a noindex tag on blocked sites because it cannot browse them.
A robots.txt file can tell web crawlers to ignore, for example, login pages, personal archives, or pages resulting from unique classes and filters. Keep the crawl time of the crawlers on the parts you want to rate.

